December 2, 2025
Beginner’s Guide to Algebra: Everything You Need to Get Started
Algebra is one of the most important building blocks in mathematics. Whether you are a student beginning your math journey, an adult revisiting foundational skills, or someone preparing for competitive exams, learning algebra opens the door to logical thinking, problem-solving, and advanced mathematics. This comprehensive beginner-friendly guide covers what algebra is, why it matters, fundamental concepts, step-by-step examples, and essential practice habits to help you master the basics with confidence.
What Is Algebra?
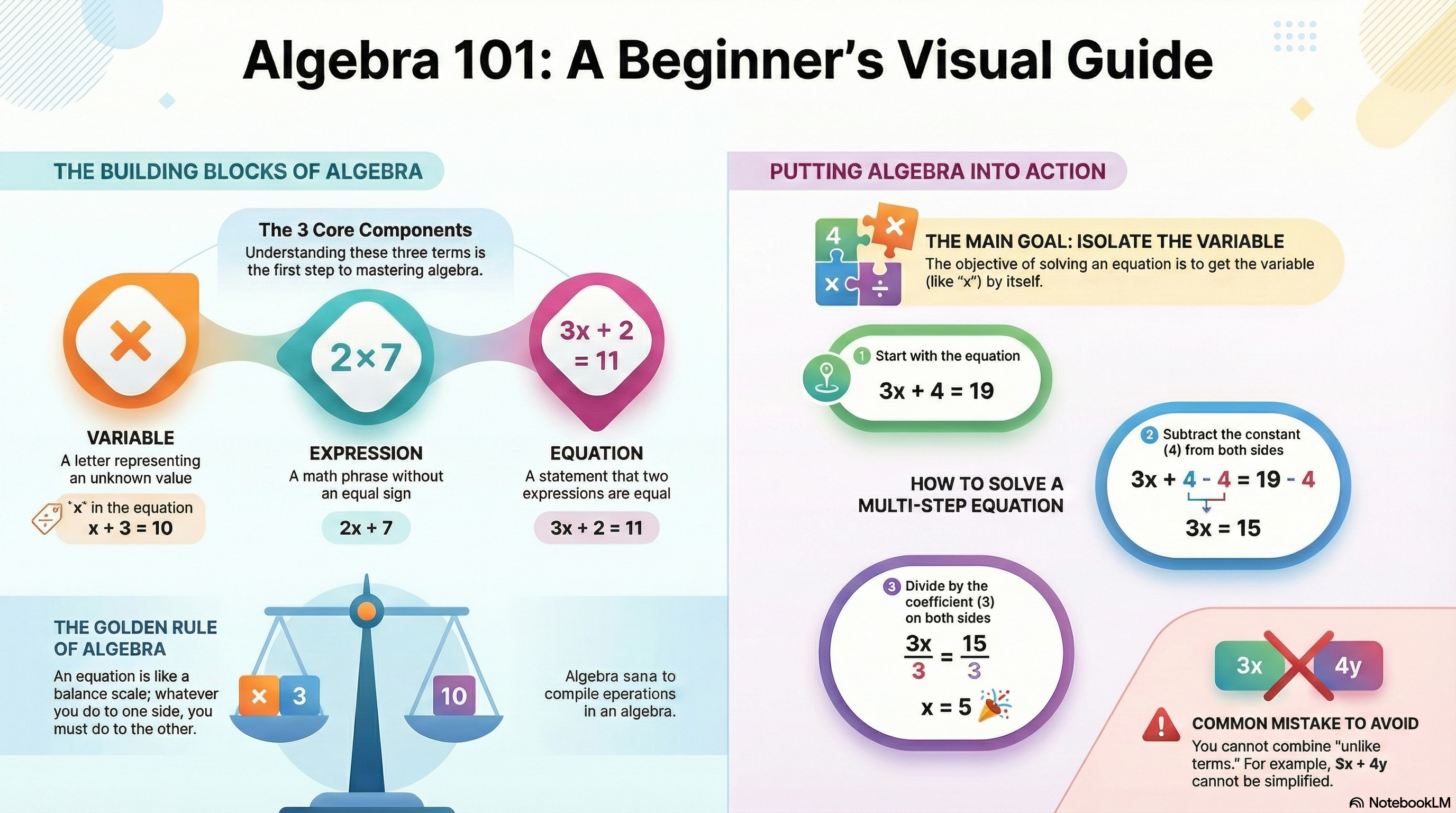
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that uses symbols, primarily letters, to represent numbers and relationships. These symbols are known as variables.
Why Algebra Matters
Algebra helps you:
- Solve real-world problems using equations
- Understand patterns and relationships
- Develop analytical and logical thinking
- Prepare for higher-level math like calculus and statistics
- Strengthen decision-making and problem-solving skills
Key Terms to Understand
Before diving deeper, memorize these essential algebra terms.
Variable
A letter that represents an unknown value.
x + 3 = 10
Constant
A fixed number that never changes.
7, 12, -4
Expression
A combination of numbers and variables without an equal sign.
2x + 7
Equation
A statement showing two expressions are equal.
3x + 2 = 11
Coefficient
A number multiplied by a variable.
The coefficient in 5x is 5.
Term
A part of an expression separated by plus or minus signs.
In 4x - 7 + 2y, the terms are 4x, -7, 2y.
The Balance Rule of Algebra
An equation behaves like a balance scale.
Whatever you do to one side, you must also do to the other.
This is the foundation of solving equations correctly.
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Before solving equations, learn to simplify expressions.
Combining Like Terms
Like terms have the same variable and power.
3x + 5x = 8x
7y - 2y = 5y
Unlike terms cannot be combined.
3x + 4 (cannot combine)
2x + 3y (different variables)
Distributive Property
Used when multiplying across parentheses.
a(b + c) = ab + ac
Example:
3(2x + 5) = 6x + 15
Solving Linear Equations
A linear equation involves a variable with a power of 1.
The goal is to isolate the variable.
Example 1: Simple Equation
x + 7 = 15
x = 8
Example 2: With Coefficient
4x = 20
x = 5
Example 3: Multi-Step Equation
3x + 4 = 19
3x = 15
x = 5
If you want to practice solving similar problems, you can use our free Algebra Calculator here:
https://globalcalcbox.cloud/category/algebra
Example 4: Variables on Both Sides
5x - 4 = 3x + 10
2x = 14
x = 7
Inequalities
Inequalities show non-equal relationships.
Symbols include:
greater than
- < less than
= greater than or equal to
- <= less than or equal to
Example
x + 5 > 10
x > 5
Important Rule
When multiplying or dividing by a negative number, flip the inequality sign.
-3x < 9
x > -3
Algebraic Word Problems
Word problems connect algebra with real-life logic.
Example 1: Savings Problem
A laptop costs 700. You save 50 each week.
Let x = number of weeks.
50x = 700
x = 14 weeks
Example 2: Distance Problem
Formula: distance = speed × time
Speed = 60 km/h
Time = 3 hours
Distance = 60 × 3 = 180 kmExample 3: Profit Problem
Profit = selling price – cost price
180 - 120 = 60Introduction to Functions
A function assigns exactly one output for every input.
Function notation:
f(x) = expressionExample:
f(x) = 2x + 3
f(2) = 7
Graphing Linear Equations
Linear equations are often written as:
y = mx + bWhere:
- m = slope
- b = y-intercept
Understanding Slope
Slope indicates steepness.
slope = rise / runIf slope = 2, for every step right, the line moves 2 units up.
Understanding the Y-Intercept
The y-intercept is where the line crosses the Y-axis.
y = 3x + 4
slope = 3
y-intercept = 4
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Combining unlike terms
- Forgetting to flip inequality signs
- Doing different operations on each side
- Mixing up expressions and equations
- Ignoring negative signs
Best Practices for Learning Algebra Faster
- Practice daily
- Write every step clearly
- Start simple before moving up
- Use real-world examples
- Quiz yourself regularly
- Ask questions whenever confused
Quick Reference Table
Concept Meaning Example
Concept | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
Variable | Unknown value | x + 3 |
Coefficient | Multiplier of a variable | 5 in 5x |
Expression | No equals sign | 2x + 7 |
Equation | Has an equals sign | 3x + 2 = 11 |
Slope | Steepness | slope = rise/run |
Function | Input-output relationship | f(x) = x + 2 |
Final Thoughts
Algebra may feel challenging initially, but with practice and a clear understanding, anyone can master it. This guide introduced core concepts, examples, and beginner-friendly explanations to help you build a strong foundation in algebra.